Most Used Python IDEs and Code Editors

Python has become one of the most prominent programming languages in the world today. This has been attributed to its ease of use and its broad avenue of applications ranging from data science to artificial intelligence to web development. If you are looking for a guide to the best code editors to use in your Python development environment, then this is the perfect one for you! In this article, let’s check out the popular IDEs and code editors that can assist you with all your Python programming requirements.
IDE vs Code Editor
IDE stands for Integrated Development Environment. An IDE is a software program that combines all the common developer tools in a single user interface: a source code editor, a code debugger, local build automation, code completion functionalities, and sometimes code autosave capabilities. Some code completion and automatic code generation tools supported in IDEs include sophisticated artificial intelligence tools like qodo (formerly Codium) and Github Co-Pilot. An IDE should however not be confused with a code editor.
A Code Editor is a tool that facilitates code editing and makes it easier by providing features such as syntax highlighting and code formatting. A code editor differs from an IDE in that they have fewer features outside of their primary use case of writing and formatting code. The fewer features in code editors make them typically quicker and lighter weight. However, some code editors deliver additional functionality, like debugging and code execution, making them preferred by some developers over IDEs.
Benefits of IDEs for Developers
One of the main zen of Python is “Simple is better than complex”. In this regard, there’s no sense in doing repetitive tasks if you can automate them. IDE’s help in this regard. IDEs and code editors deliver several benefits to developers making the software development journey less painful including:
- Syntax Highlighting and Error Highlights – IDEs highlight erroneous code blocks to allow a developer to rectify them. IDEs also help to locate symbols and strings you’re looking for in less time in a code base.
- Autosaving Files – Most Python IDEs have an autosave feature that allows a developer to work on a software codebase until it’s quitting time and then the IDE will help to pick up where you left off automatically.
- Code Running – IDEs provide an easier isolated interface to run the written code without moving to another application to test the code.
- Code Debugging– IDEs provide a thorough debugging environment that enables developers to identify and fix errors in their code quickly as they write. IDEs offer debugging tools like breakpoints, call stack analysis, and variable inspection that make it easier for developers to find and fix problems in their code.
- Code and Project management – IDEs offer tools to manage code like version control using various tools like Git, Mercurial, CVS, Bazaar, etc. This allows developers to track changes in their code, roll back code changes, and collaborate with other developers efficiently. Furthermore, IDEs offer project management tools that enable developers to manage a large project with many lines of code and functions especially in a situation where multiple developers are working on the same codebase at the same time.
- Code Formatting – IDEs provide integrated code formatting mechanisms that reclaim countless hours since code is automatically arranged in the proper format.
- Code Integration – IDEs provide an avenue to integrate the written code with other tools and services e.g. deployment tools and code testing frameworks which help developers to automate most repetitive tasks and improve their CI/CD workflows.
As a Python software developer, you often need additional tools to work efficiently, like language support or source code control depending on your specific situation. If you are unsure of which IDE or code editor is best for you, we’ve got you covered. Here are the top Python IDEs and code editors you should look into.
-
PyCharm
PyCharm is a proprietary Python IDE solution. Pycharm is developed by JetBrains, which develops a suite of code editors for other languages in addition to Python. PyCharm is compatible with macOS, Linux, and Windows, so you can use it across systems.
There are two versions of the tool: a free open-source edition and a paid version. So, if you’re looking for a free Python IDE, this might be your ticket.
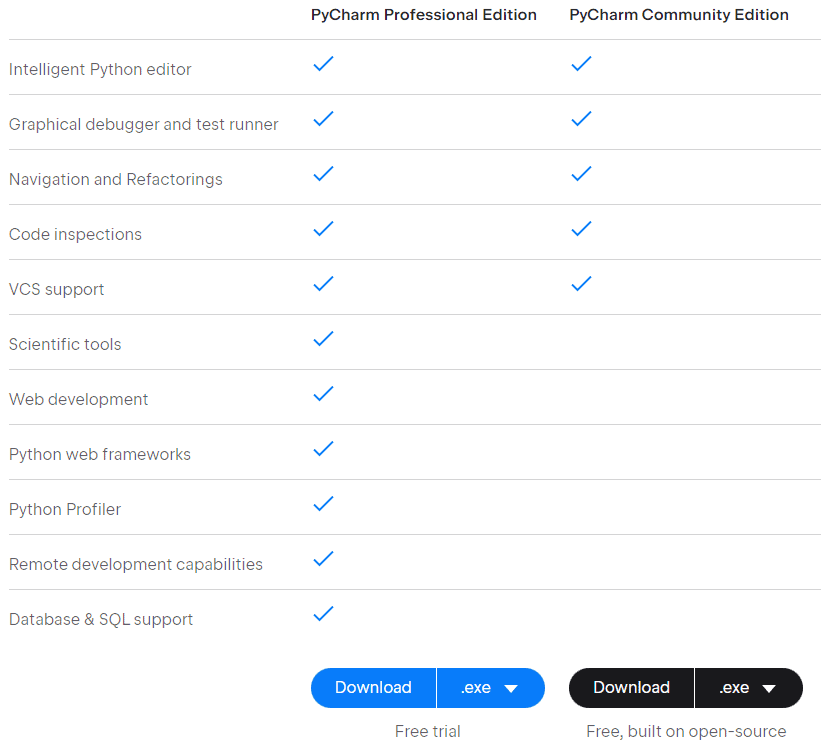
If you choose the paid version, you’ll get advanced features like database and SQL support, remote development capabilities, and scientific tools. Featuring a sleek and intuitive UI, here’s what you can expect to see when you try to make a new project in Pycharm:
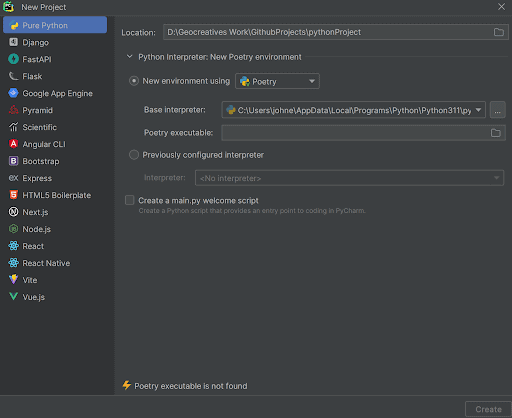
PyCharm advertises itself as a platform that brings all the Python development tools you need together in one location. It offers basic intelligent code completion, saving you time and freeing you from monotony or repetitive tasks and quick bug fixes. The platform also offers support for several popular web development frameworks, like FastAPI, Django, Pyramid, Flask, and Google App Engine. In addition, PyCharm supports several languages in addition to Python, including JavaScript, Node.js, HTML/CSS, SQL, and JavaScript frameworks like VueJS, ReactJS, and Angular. Whether you’re interested in the open-source version or the professional edition, you can get started for free.
-
Visual Studio Code
Visual studio code is an open-source code IDE developed by Microsoft. It is written in Electron and works across major operating systems including MacOS, Linux, and Windows. It has a beautiful modern UI owing to its development by the highly skilled designers and developers at Redmond.
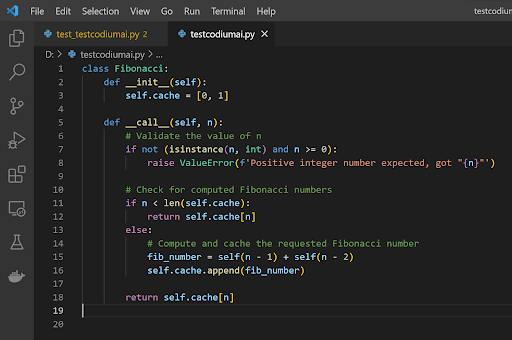
As an open-source solution, VS Code offers several powerful tools out of the box, including an intelligent autocompletion feature, a built-in debugger, and built-in Git commands, among other things. Since it’s open source, it’s also extensible creating a sea of plugins to enhance the IDE like Docker support. Search a seemingly endless number of integrations and plugins to make your VS Code experience that much stronger.VS Code integrations can be enabled or disabled at will. VS Code multiple programming languages and frameworks besides Python, including JavaScript, Markdown, Ruby, C++, Go, PHP, Java, and numerous others.
-
Spyder
Spyder is an open-source IDE originally created by Pierre Raybaut for scientific Python development workflows that work across macOS, Linux, and Windows environments. It is created specifically for data science, research, and scientific computing.
Spyder offers a range of features, such as an interactive Python console, a debugger, a variable explorer, a code editor, and a powerful library of plugins like Spyder Notebook and Spyder Terminal, making it an excellent choice for scientific computing, research, and data analytics. Spyder supports most of the common scientific libraries like SciPy, Matplotlib, Dask, Pandas, and Numpy out of the box making it ideal for data-related workflows. If you’re a data nerd who loves seeing everything in one place, you’ll love Spyder.
Here’s an example of what your experience will look like:
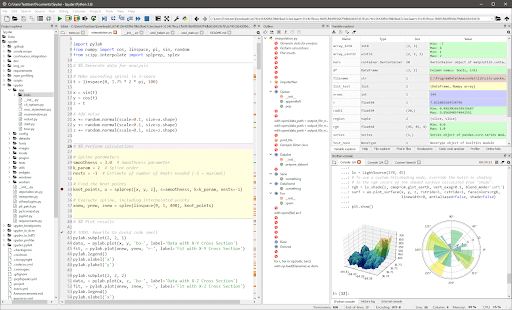
-
Jupyter Lab and Jupyter Notebooks
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web app that enables Python developers to create and collaborate on documents that include code, visualizations, narrative text, and other items. The platform is well-suited to several use cases, including data science, machine learning, statistical modeling, and data visualization.
As a developer in the scientific computing space or a bona fide data scientist, you may want to give Jupyter a spin. Jupyter is also popular among data science beginners. While Jupyter was founded as a Python editor, the platform has since begun supporting several different languages, including R, Julia, and Scala. (In fact, its name comes from supporting Julia, Python, and R!) Jupyter lets users share their work through email, Dropbox, and Github, accelerating collaboration.
The platform also works with Docker and Kubernetes to streamline deployment and installation with containerization.
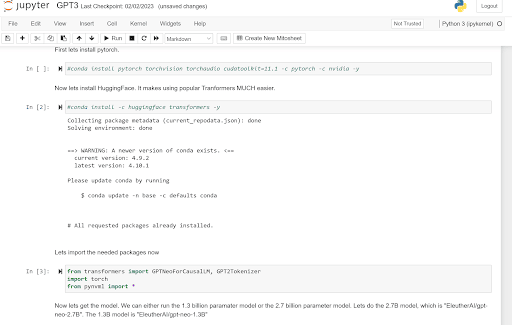
On the other hand, JupyterLab is an open-source web-based IDE that is built upon Jupyter Notebook technology. JupyterLab system supports over 100 programming languages (called “kernels” in the Jupyter ecosystem) including Python as explained in this article. It allows you to run code in a variety of ways, including running code cells within the interface, running code in a separate console, and launching interactive applications.
This is what JupyterLab looks like on start:
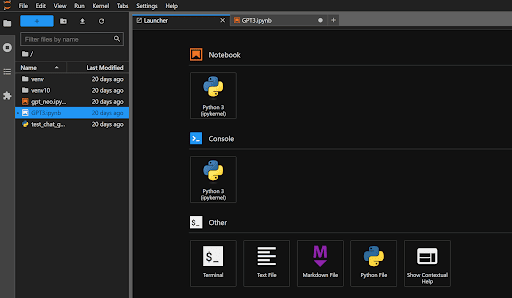
-
Emacs
Developed by Richard Stallman, Guy Steele, and David Moon, Emacs is a text editor written in its own language, Emacs Lisp, and is compatible everywhere. Emacs is a powerful, extensible, and highly customizable text editor that has been around for decades. It is widely used by programmers, system administrators, writers, and other professionals who need a versatile tool for working with text. Developers pair Emacs with Evil, a complete emulation of Vim’s multi-model editor, and the results are impressive.
One of its greatest strengths is its ability to support multiple programming languages and file types, including C++, Python, HTML, and LaTeX. The main disadvantage of Emacs though is that it has a steep learning curve and its download process for Windows OS is not direct. If you want to master Emacs, expect to spend a while getting to know it.
-
Sublime Text
Sublime Text is a proprietary sophisticated text editor compatible across macOS, Linux, and Windows environments. Sublime Text is free to test, you need to buy a license to use it continuously. That said, the company doesn’t enforce a time limit. So, in theory, you could use it for free in perpetuity. But the developers probably deserve to be paid, especially if you end up using the tool for a while, so proceed wisely. Since Sublime Text is proprietary, you can’t edit its internals or view the source code thus it shouldn’t come as a surprise that, despite its age, Sublime doesn’t offer a robust marketplace of plugins and integrations. However, what the editor lacks in plugins, it wins in terms of power and speed. It also comes with great features out of the box for example multiple cursors.
-
Vim
Vim (i.e., Vi iMproved) was created by Bram Moolenar in 1991 as a rewrite of the older Vi that Bill Joy developed back in the ‘70s. It is written in its own language (Vimscript) and is compatible everywhere. Vim is an excellent choice for developers who enjoy performing every action directly from the keyboard without having to use a mouse.
Vim is designed to be efficient and flexible, with many powerful features and commands that can help developers quickly and easily navigate, edit, and manipulate text. One of the main powers of Vim is that a user can record a macro and replay them to automate repetitive tasks.
Vim was once notorious for being hard to quit. When you open up Vim today, you’ll see a “:q to quit” message in the lower left-hand corner. That was added quite a bit after Vim launched.
But even with the slow advancements, you’ll be rewarded for getting to know Vim. Competent Vim users will blaze past previous speeds at which they previously edited text.
Master Vim’s commands and you can do amazing things. But everything has a cost. If you’re looking at a big project in your immediate future and need to get up and running fast, you’re far better off with one of the editors above. Why? Look at the basic commands you need to know to use Vim, and you’ll realize it will take you months to get comfortable with them.
-
Dataspell
JetBrains DataSpell is an addition to the JetBrains IDEs. It is a cutting-edge integrated development environment (IDE) specifically designed for data scientists and analysts. With its extensive set of tools and features, DataSpell simplifies the process of working with data, enabling users to efficiently clean, visualize, and analyze datasets thus making it an indispensable tool for data-driven professionals.
Some of the key features of JetBrains DataSpell are:- Designed for data scientists and analysts with high interactivity and smart coding assistance
- Supports Python, R, and SQL programming languages.
- Seamless integration with local and remote Jupyter, JupyterLab, and JupyterHub servers.
- Data cleaning and visualization tools with a scientific Python console for live outputs.
- Advanced code refactoring and debugging
- Built-in version control system
- Collaborative features for team-based projects
- Extensive library support and customizability
-
NeoVim
NeoVim is a hyperextensible modern fork of the Vim text editor. It was created in 2014 to modernize Vims architecture for maintenance and extensibility. It is fully compatible with most of the Vims plugins while adding new features and improvements.
NeoVim has a built-in terminal emulator which makes running shell scripts easy. NeoVim has 30% less code than Vim and thus provides a faster and more flexible editing experience than Vim. At the same time, it makes it easier for developers to extend the editor for their specific use cases. Here is an example of the default NeoVim interface in Windows 11.
The above IDEs are the most commonly used Python IDE’s and editors. Furthermore, below is a list of other tools worthy of mentioning when dealing with Python editing.
Other Noteworthy Mentions
-
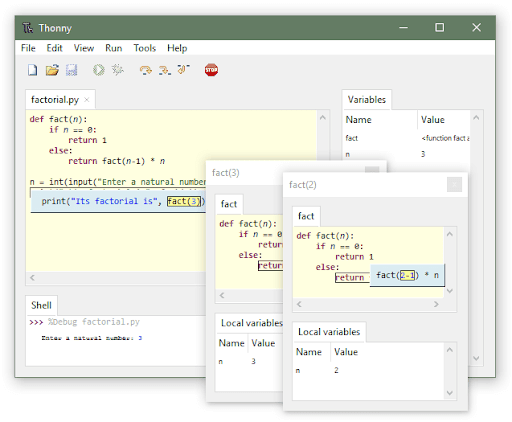
Thonny
Thonny is a beginner-friendly IDE for Python that comes with Python 3.x bundled. So once you install Thonny you start writing Python code. It is open source and provides a simple and intuitive user interface for writing and running Python code. It is available for all major operating systems, and it is free. One of the key selling features of Thonny is that it has an inbuilt Python tutor which helps beginners come to speed with Python using interactive examples.
-
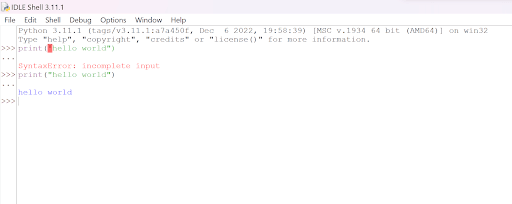
IDLE
Python Integrated Development and Learning Environment (IDLE) is an interactive development environment that comes bundled by default with the Python programming language in all the major operating systems. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for editing and running Python code, making it easier for beginners to get started with Python programming. Here is what it looks like for Python 3.11 running in Windows 11 OS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, every Python developer has their own unique strengths, and you know yourself better than anyone else. Take your time and test out several tools to see what works best for you. Once you’ve found the perfect match, you’ll be able to write better code faster—which means you’ll have more time to spend building applications that solve important problems.
The decision to select a specific IDE or code editor is influenced by various factors, such as budget, the nature of your work, your experience, and personal preferences. To help you make an informed choice, consider the following suggestions based on your area of expertise:
- Software Developers– Opt for PyCharm or Visual Studio Code to access a robust set of tools tailored for general programming tasks.
- Data Scientists– Utilize JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebooks, or DataSpell to streamline data manipulation, visualization, and analysis.
- Vim Enthusiasts– Choose Vim or NeoVim to take advantage of familiar keybindings and a highly customizable environment.
- Scientific Computing Specialists– Select Spyder or DataSpell for a specialized IDE that caters to the unique needs of scientific research and computation.
Ultimately, the right IDE or code editor for you will depend on your specific needs and preferences, but exploring these options based on your field can help guide you to a more efficient and enjoyable coding experience.



